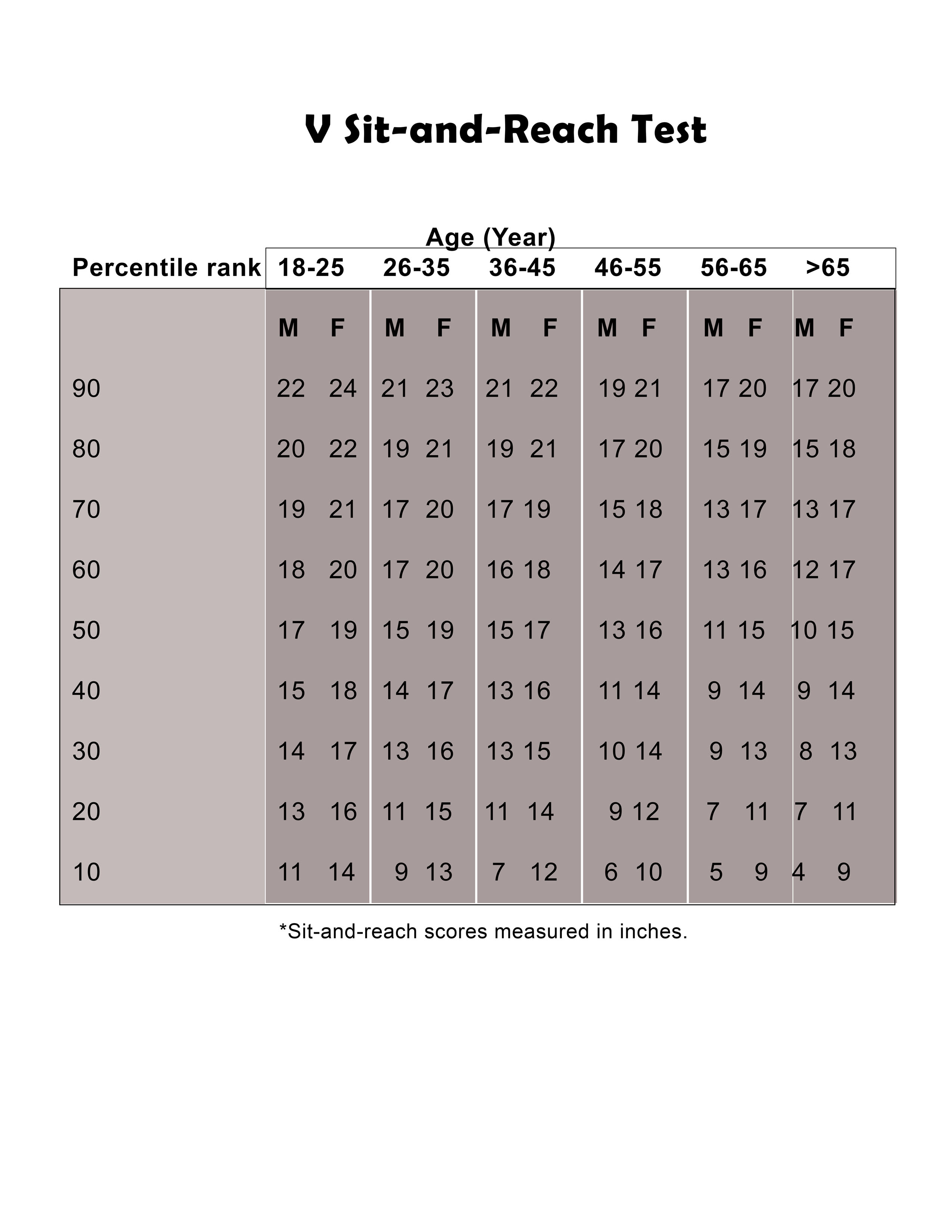
Here's an exercise to test your shoulder flexibility.
Stand and raise your left arm overhead and bend your left elbow so that your left hand points down the upper spine between the shoulder blades (hand should also be able to touch the opposite shoulder blade). Bring your right arm behind the back, and bend the right elbow so the fingers point up the spine, between the scapulae. Good flexibility of the right shoudler exist if fingertips of both hand can touch. Change sides.
Stand and raise your left arm overhead and bend left elbow so that left hand points down the upper spine between the shoulder blades (hand should also be able to touch the opposite shoulder blade) Bring your right arm behind the back, and bend the right elbow so the fingers point up the spine, between the scapulae.
Good flexibility of the right shoulder exist if fingertips of both hand can touch. Change sides and repeat.
Shoulder Girdle Flexibility
Shoulder elevation
Equipment: Hard surface; straight stick or ruler; measuring tape; partner.
Starting Position: Assume a prone (face down) position with the arms straight, about shoulder width apart. Grasp the stick in both hands.
Movement: While keeping the chin o the floor and arms and wrists straight, lift the stick up as high as possible. Your partner measure the distance in inches from the bottom of the stick to the floor. Use the best score form three trails.
Shoulder Elevation________________inches.
Arm Length______________________inches.
Scoring: Multiply the best measurement by 100 and divide the product by the arm length in inches. Are length is measured from the acromion process to the upper surface of the stick which is being held as the arms hang downward.
Shoulder elevation____________ x 100 / arm length = Adjusted Shoulder Elevetion
Score__________
|
|
Below Average |
Average |
Above Average |
Outstanding |
|
Women |
76 or below |
77-101 |
102-112 |
113-123 |
|
Men |
78 or below |
79-102 |
103-113 |
114-123 |
|
Get MORE: Personal Trainer Forms, Consent Forms, Exercise Log Sheets, Questionnaires, Charts & MORE. (Click link below) |


 he/she is not already warmed up) and perform some static stretching, particularly of the hamstrings, low back and calf muscles.
he/she is not already warmed up) and perform some static stretching, particularly of the hamstrings, low back and calf muscles.